
- Introduction to PRINCE2
- History and Background
- PRINCE2 Principles
- PRINCE2 Themes
- PRINCE2 Processes
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Benefits of PRINCE2 Certification
- PRINCE2 vs PMP
- Exam and Certification Details
- Applications in Project Management
- Conclusion
Eager to Acquire Your Data Science Certification? View The Data Science Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Introduction to PRINCE2
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a widely adopted and formal project management methodology used extensively across a variety of sectors, including IT, construction, healthcare, finance, and government. It offers a comprehensive and scalable framework for managing projects in a consistent, process-driven, and structured manner, ensuring clarity, control, and successful outcomes throughout the project lifecycle. PRINCE2 emphasizes clearly defined roles and responsibilities, a stage-by-stage approach, and key control points, making it suitable for both small-scale initiatives, large, complex programs, and structured Data Science Training projects. The methodology is built on seven core principles, seven themes, and seven processes, all of which are based on industry best practices and real-world project experience. This structured approach facilitates proactive risk management, ongoing progress monitoring, and comprehensive documentation, which together help keep projects aligned with strategic goals and on schedule. PRINCE2 encourages flexibility and adaptability, allowing it to be tailored to the unique needs of different organizations and project types.
History and Background
PRINCE2 was derived from PROMPT II, an IT project management approach created in 1975 by the UK government. 1989 PROMPT II transformed into PRINCE (Projects IN Controlled Environments), which was adopted by all UK government projects. To increase the framework’s flexibility to other IT projects, PRINCE2 emerged in 1996. PRINCE2 was developed to be sector-agnostic and to be applied to several sectors. The approach was subsequently enhanced and revised in 2009 and 2017 to improve flexibility, applicability, and emphasis on customization. PRINCE2 is utilized by organizations globally and is considered a top project management standard today.
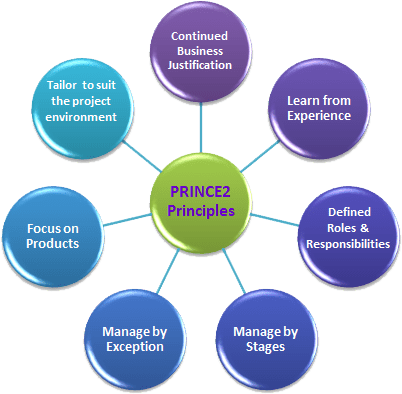
PRINCE2 Principles
The seven core principles of PRINCE2 Project Management guide its implementation and ensure that projects are effectively managed:
- Continued Business Justification: Projects must have a clear business case with ongoing justification.
- Learn from Experience: Project teams should use lessons learned from previous projects to improve future outcomes.
- Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Clear roles and accountability ensure everyone understands their responsibilities.
- Manage by Stages: Projects are divided into manageable stages to ensure effective control and decision-making.
- Manage by Exception: Tolerances are set for time, cost, and quality, enabling managers to focus on deviations from the plan.
- Focus on Products: The methodology emphasizes delivering quality products that meet project objectives.
- Tailor to Suit the Project: PRINCE2 is flexible and should be adapted to the project’s size, complexity, and environment.
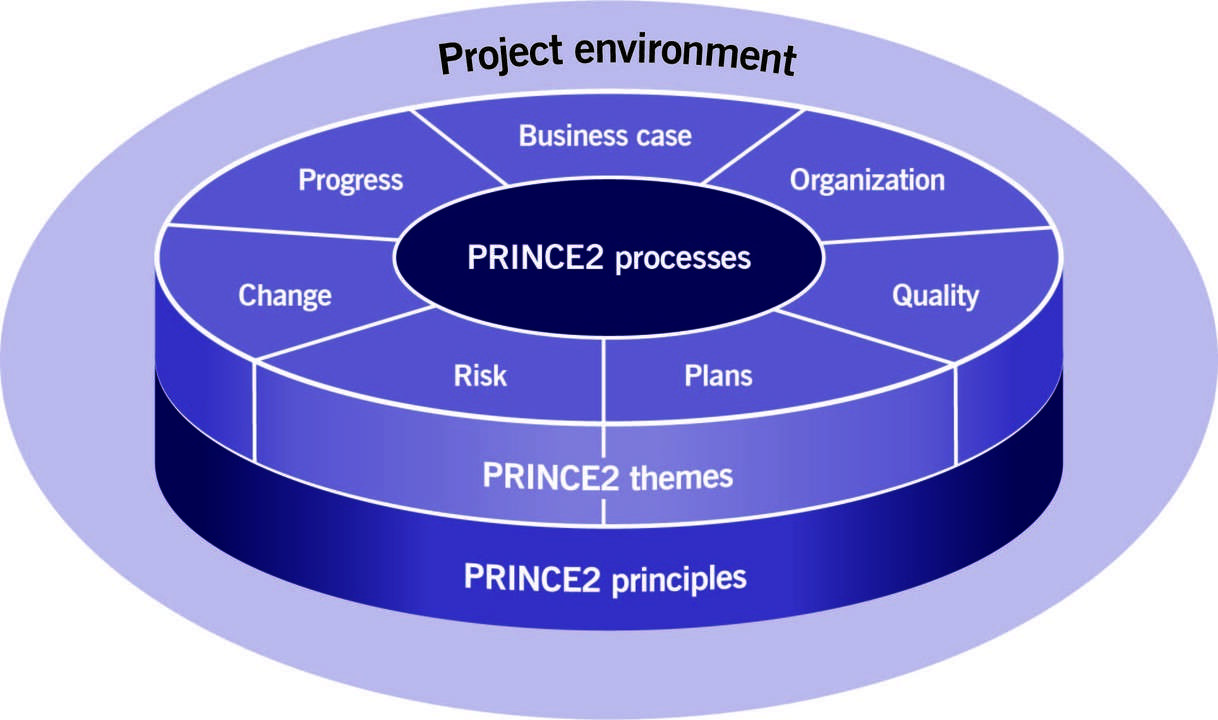
PRINCE2 Themes
- Business Case: Defines the justification for the project, including benefits, costs, and risks.
- Organization: Establishes the project team structure, including roles and responsibilities.
- Quality: Ensures the products meet specified quality requirements through regular checks.
- Plans: Outlines the steps, timelines, and resources needed to achieve project objectives.
- Risk: Identifies, assesses, and mitigates potential risks throughout the project lifecycle.
- Change: Manages changes and issues effectively to avoid project disruptions.
- Progress: Monitors and controls the project’s performance and progress against the plan.
- Starting Up a Project (SU): The preliminary phase assesses the project’s viability. It involves defining the business case, appointing the project board and manager, and identifying the necessary resources. The goal is to determine whether the project is worthwhile before committing to further planning.
- Directing a Project (DP): This process provides high-level oversight by senior Project Management . The Project Board makes key decisions, authorizes project stages, and ensures the project aligns with business objectives. It also involves resolving escalated issues and approving significant changes.
- Initiating a Project (IP): The project is formally planned and structured. During this phase, the team defines the project plan, controls, and risk management strategies. A detailed initiation document outlines the scope, objectives, and governance framework.
- Controlling a Stage (CS): This process focuses on the day-to-day management of each project stage. The project manager monitors progress, resolves issues, and ensures quality. The project Board receives regular updates, and corrective actions are taken if necessary.
- Managing Product Delivery (MP): The project team, guided by Product Management with agile practices, develops and delivers the products, ensuring that they meet quality standards and deadlines. The project manager oversees the handover of products and verifies compliance with the requirements.
- Managing a Stage Boundary (SB): At the end of each stage, the project board reviews the progress to decide whether to continue, revise, or close the project. This process involves evaluating performance, identifying issues, and planning the next stage.
- Closing a Project (CP): The final process formally closes the project. The deliverables are accepted, and a project review is conducted to capture lessons learned. All documentation is finalized, and responsibilities are transferred to the business for ongoing operations.
- Executive: Ensures the project delivers business value.
- Senior User: Represents the end-users and ensures the product meets their needs.
- Senior Supplier: Provides expertise and resources for product delivery.
- The board approves stages, resolves escalated issues and ensures alignment with business objectives.
- Clients: The recipients of the final deliverable.
- Sponsors: Those funding the project.
- Users: The end-users who will interact with the product.
- Stakeholders influence project requirements and provide feedback throughout the lifecycle.
- Global Recognition: PRINCE2 is a widely recognized certification that enhances career prospects globally.
- Improved Project Management Skills: It provides a structured approach to managing projects efficiently.
- Increased Employability: PRINCE2 certification is valued by employers across various industries.
- Standardized Processes: Enhances consistency and efficiency in project execution.
- Risk Management: Improves the ability to identify and mitigate risks effectively.
- Better Communication: Promotes clear roles and responsibilities, improving stakeholder collaboration.
- Scalability: Suitable for projects of all sizes, from small initiatives to large programs.
- IT and Software Development: Managing complex IT projects with structured processes.
- Construction: Ensuring quality control and risk management in large-scale projects.
- Government and Public Sector: Standardizing processes in government projects.
- Healthcare: Managing healthcare initiatives with controlled stages and quality checks.
- Finance and Banking: Enhancing project governance and compliance.
Excited to Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
PRINCE2 Processes
Roles and Responsibilities
PRINCE2 Roles
Project Board: The project’s governing body is responsible for decision-making and oversight. It consists of:
Project Manager: The central figure responsible for day-to-day operations handles planning, scheduling, resource allocation, and Risk Management. The project manager ensures the project stays on track and meets deadlines and quality standards.
Team Manager: This role handles the technical execution of tasks. The team manager oversees the development and delivery of products, ensures quality compliance, and reports progress to the project manager.
Project Assurance: This role independently monitors the project’s quality, business case, and risk compliance. It ensures the project adheres to the defined processes and standards without being directly involved in execution.
Project Support: This department provides administrative support, such as documentation, reporting, and record-keeping. It also assists in organizing meetings, maintaining logs, and managing project files.
Stakeholders: Individuals or groups with an interest in the project’s outcome. This includes:
Interested in Pursuing Data Science Master’s Program? Enroll For Data Science Master Course Today!
Benefits of PRINCE2 Certification
Obtaining PRINCE2 certification offers several advantages for professionals and organizations:
Preparing for a Data Science Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer
PRINCE2 vs PMP
PRINCE2 and PMP (Project Management Professional) are both well-recognized project management certifications, but they differ significantly in approach and structure. PRINCE2 is a methodology that provides defined processes and step-by-step guidance, whereas PMP is a framework grounded in knowledge areas and process groups, offering broader principles rather than fixed steps. Originating in the UK, PRINCE2 is commonly used in public sector projects, while PMP, developed by the U.S.-based Project Management Institute (PMI), has global recognition, particularly in private sector industries such as IT, construction, and finance. PRINCE2 emphasizes structured processes with clearly defined stages and roles, while PMP centers on knowledge areas like scope, cost, and risk, grouping processes into stages such as planning and execution. Both frameworks can complement Data science Training by providing structured approaches to manage projects effectively. When it comes to certification requirements, PRINCE2 is more accessible to beginners as it does not require prior project management experience, whereas PMP demands specific experience and education hours, making it more suited for seasoned professionals. The exam format also differs; PRINCE2 includes two exams Foundation and Practitioner while PMP involves a single, comprehensive exam. Additionally, PRINCE2 offers tailoring options for organizations to adapt the methodology to their needs, whereas PMP provides a more standardized approach for consistency across various industries and projects.
Exam and Certification Details
| Certification Level | Purpose | Exam | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRINCE2 Foundation | Introduces the basic principles, themes, and processes of PRINCE2 | 60 multiple-choice questions, 60 minutes, 55% passing score (33 correct answers). | Beginners, project team members, or anyone seeking foundational knowledge of PRINCE2. |
| PRINCE2 Practitioner | Validates the ability to apply PRINCE2 in real-world project scenarios | 68 scenario-based questions, 150 minutes, 55% passing score (38 correct answers) | Experienced project managers or professionals aiming to lead PRINCE2-based projects. |
Applications in Project Management
PRINCE2 is widely applied in various industries, project types, and by professionals such as Software developer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) offers a structured and scalable project management methodology that has proven to be highly effective in managing projects across various sectors. With its emphasis on clear roles, defined processes, and robust control mechanisms, PRINCE2 provides organizations with the tools needed to deliver projects successfully, on time, and within budget. Whether applied in IT, construction, healthcare, finance, or government sectors, PRINCE2’s adaptability ensures it can be tailored to fit the specific needs and complexity of any project. The PRINCE2 certification enhances the career prospects of project managers by equipping them with a globally recognized qualification that validates their expertise in project management, while complementary skills like Data Science Training further broaden their analytical capabilities and decision-making proficiency. By following the seven core principles, themes, and processes of PRINCE2, professionals can ensure that their projects are aligned with business goals, stakeholder expectations, and quality standards. PRINCE2’s comprehensive approach, when combined with its clear division of responsibilities, ensures that projects are managed with precision and clarity, reducing risks and enhancing collaboration. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for skilled PRINCE2-certified professionals is expected to grow, making it a valuable credential for anyone in the field of project management. Whether you’re a newcomer looking to build your project management skills or an experienced professional aiming to refine your expertise, PRINCE2 offers a structured path toward success in the project management domain.


